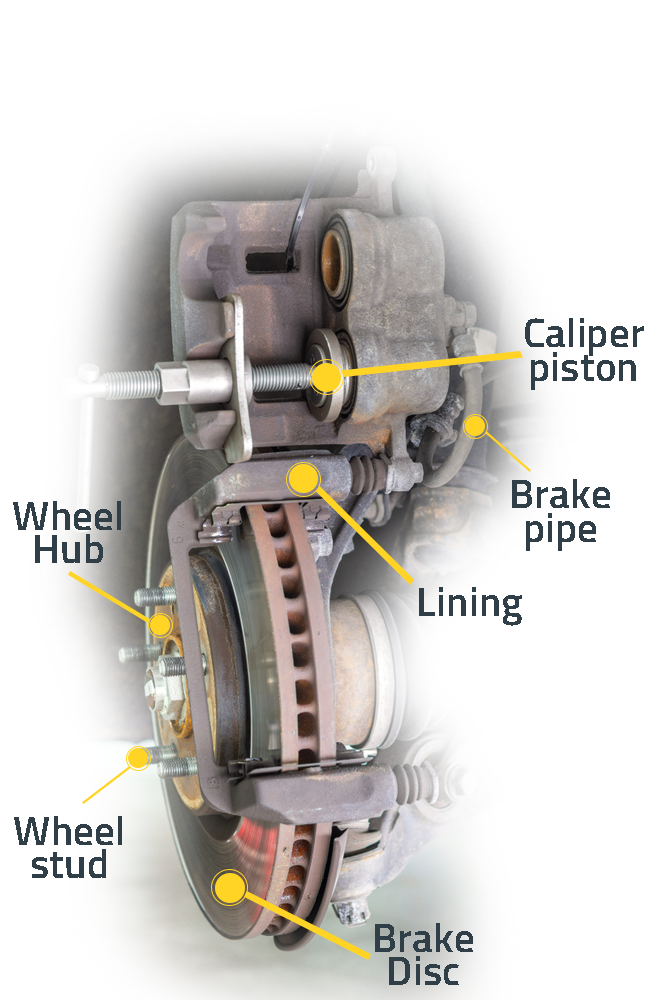
What is Brake Caliper?
The brake caliper is a hydraulic part that looks like a hand grips the disc when viewed from the outside and creates braking. it can be seen that the caliper is painted in colors such as red and blue on some vehicles,
How Does the Brake Caliper Work?
When the brake pedal is pressed, the pressurized brake hydraulic oil coming from the brake hydraulic pipes and hoses enters through the connection union in the brake caliper, acts on the piston inside the caliper cylinder and pushes the piston forward, causing the pads to rub against the brake disc by pressing. There are two fittings in the caliper body, one is the hydraulic oil inlet union and the other is the air intake union.
There are two types of Brake caliper : With Floating Calipers and Fixed Calipers.
Construction and Operation of Floating Caliper Disc Brake
In disc brakes with floating (movable) caliper, the caliper carrier is fixed and the caliper (with its piston) is movable. In a floating caliper brake system, the caliper only has a piston on one side. When the brake pedal is pressed, pressure is created on the disc by the piston moving forward. The parts of the floating caliper disc brake are; Caliper and piston (movable), caliper carrier (bracket) fixed, caliper slider pins (two), pad holder clips, gasket and bellows, washers, etc. Floating caliper disc brake features; very simple structure, light weight, dirt-proof, easy to disassemble, change the pads, the most common use is the caliper type floating caliper disc brakes. Floating caliper disc brake features; very simple structure, light weight, dirt-proof, easy to disassemble, change the pads, the most common use is the caliper type floating caliper disc brakes.
Caliper Pin (Slipper pin)
The brake caliper moves back and forth thanks to the caliper pins, the caliper pins are also called "slipper pins". The caliper pins are protected by a dust boot and slide with grease. The grease used in caliper pins is usually silicone-based grease, it should be high temperature resistant and waterproof. It is usually sold in tubular form under the name "caliper pin grease".
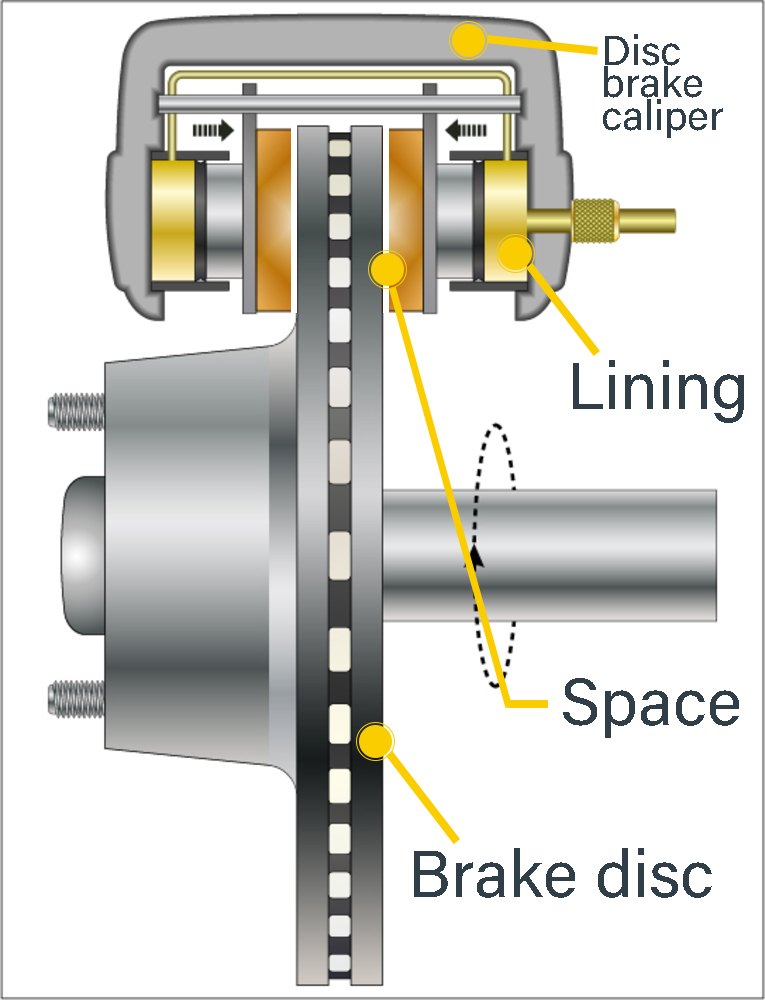
Construction and Operation of Fixed Caliper Disc Brake
In the fixed caliper brake system, the caliper carrier and the caliper are fixed. In this system, there are caliper pistons on both sides of the brake disc. In other words, floating caliper brake has a single caliper piston and the caliper works by moving; In the fixed caliper system, there are two caliper pistons (in front of and behind the disc) and the caliper does not move and is fixed.
(Fixed Caliper)
When the brake is pressed, the opposite caliper pistons on the front and rear surfaces of the disc move forward with hydraulic pressure, press the brake disc in the middle from both sides and brake by rubbing the pads against the disc. Brake hydraulic oil enters from the caliper inlet and acts on both pistons through the channel in the body. Features of fixed caliper disc brake; Its structure is large, air circulation is low, so it is not easy to cool (high temperature adversely affects braking), not widely used.
Disc Brake Pad Clearance Adjustment
In the caliper disc brake system, the gap between the pad-piston and the disc is about 0.15 mm. This gap between the pad and the disc is automatically adjusted, and it does not require any further adjustment. Inside the caliper cylinder is a flexible seal between the cylinder and the piston. This seal not only prevents the hydraulic oil in the cylinder from leaking out (sealing), but also keeps the pad-disc gap constant as a consequence to its flexible structure
(Piston bellows and brake clearance adjustment)
The piston seal adjusts the clearance as follows: The brake pedal is depressed, the hydraulic oil pushes the piston forward. With the forward movement of the piston, the part of the felt, which is fixed in the inner part of the cylinder, in contact with the piston, is stretched forward by the amount of movement of the piston. When we pull on an elastic material, it stretches and when we let go, it immediately returns to its original shape (like a flexible rubber). Here, too, the piston seal, which stretches during braking, is in a loaded-tensioned state and wants to return to its original state immediately when the brake pedal is released. When the brake pedal is released and the hydraulic pressure drops, the piston bellows retracts the piston as far as it flexes,this distance is the brake gap. Over time, the pads wear and this wear requires the pad to travel more distance to reach the disc, that is, the gap between the pad and the disc will increase, in this case, it is necessary to constantly adjust the gap as the pads wear but it is not necessary. The piston seal doesn't affect how far the piston goes, it affects how far it comes back. If the piston goes further than the piston seal stretches, the piston seal slides on the piston. When the brake is released; the piston comes back only by the amount of stretching of the seal. In other words, whether a new pad is installed or a worn out pad, when the brake pedal is pressed once, the brake gap will be adjusted thanks to this elastic piston seal.

