Causes of Brake Failures (Brakes Not Holding)
The general reasons for hydraulic brakes not holding or holding less are as follows;
*There is an oil leak in the hydraulic system, (in the caliper piston, main brake cylinder, wheel brake cylinder (if drum), brake hydraulic hose-pipe-couplings),
*Brake hydraulic system made air,
*Brake servo (hydraulic faulty)
*The shoes and pads are not installed properly in the drum brake,
*The pads are worn or oiled, or glazed from high temperature even though they are not finished
*The brake disc is tapered, cambered, or the drum has lost its roundness or bent.
Air Release of Brakes
In the brake hydraulic system, hydraulic oil circulates and creates and transmits the pressure to generate the braking force. Liquids are incompressible and transmit the same force acting on them, this principle is effectively used in the brake system. Air can be compressed, that is, when the force is applied, it flexes instead of transmitting the force, so even if the brake pedal is pressed, this movement cannot be transmitted to the brake mechanisms in the wheels. In this case, the brakes do not hold or hold very little, the brake pedal becomes quite soft. For these reasons, air formation in the hydraulic brake system is undesirable.
Causes of air in the brake system;
*As a result of the brake hydraulic oil level being too low, air entering the system from the main brake cylinder,
*The ventilation hole in the cover of the brake hydraulic oil reservoir tank is clogged,
*Leakage from the piston seals in the main brake cylinder or from the piston seals in the wheel brake cylinder, however, air entering the hydraulic system as a result of the falling pressure,
*As a result of using poor quality or wrong brake hydraulic oil, the oil boiling-evaporating and creating air in the system.
In case of air formation in the brake system, the system must be bled, the brake hydraulic oil must be refilled, if any, problem causing the bleeding must be corrected.

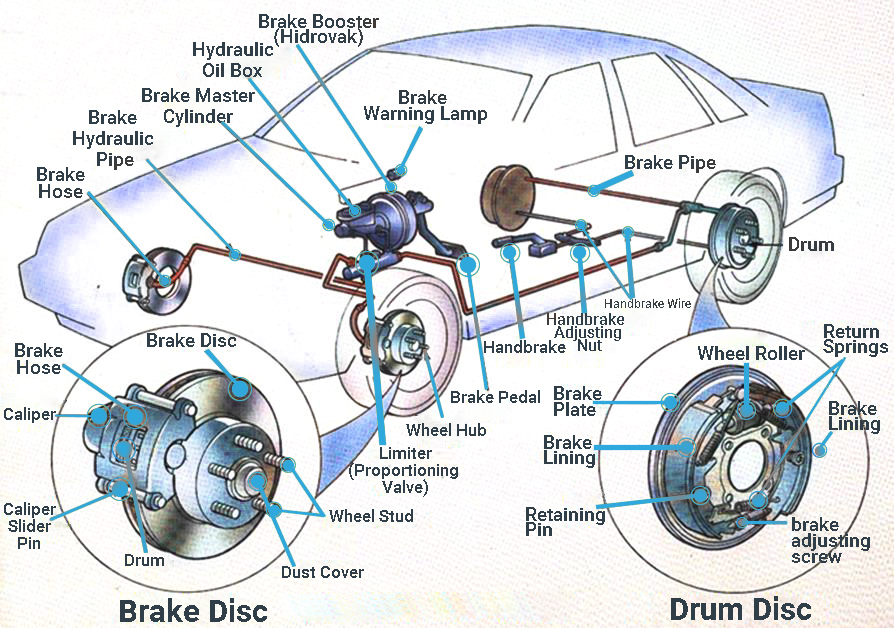
(Disc and Drum Brake System Parts)
Brakes Not Released (Brake Remains Depressed)
When the brake pedal is released, the pressurized hydraulic oil in the hydraulic system must return to the brake oil reservoir and the pressure in the line should drop, thus eliminating the force pushing the pads against the discs. If this does not happen, braking will continue.
The reasons why the vehicle continues to brake even though the brake pedal is taken off, does not release the vehicle:
*A choke in the main brake cylinder can cause high pressure in the system and prevent the brake from being released.
Main Brake center must be replaced.
*Brake servo (hydrovac) is defective,
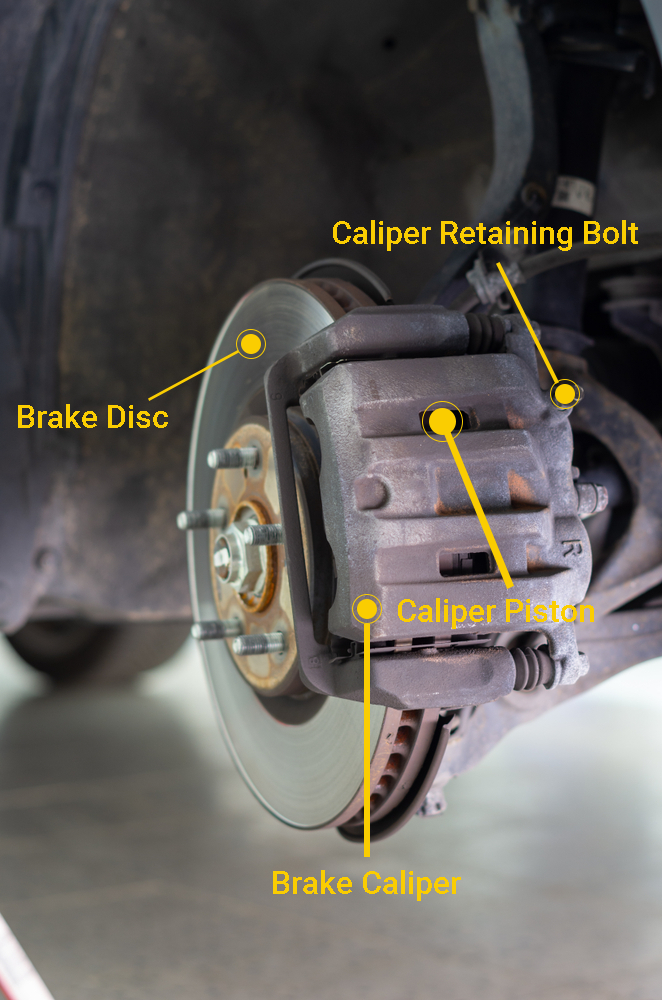
* In disc brakes, the caliper piston is stuck,
*The caliper piston seal is broken (inflexible) and cannot pull the piston back,
* Keeping the driver's foot on the brake pedal all the time,
(Brake master cylinder and brake booster - hydrowax)
The Vehicle Pulls To One Side When The Brake Is Pressed (Right-Left)
Since the braking force does not occur equally on each wheel, the vehicle pulls towards the side of the wheel where the braking force is higher.
The reasons for the vehicle to pull when the brake is applied are as follows;
* The pad of the wheel on the other side of the side the vehicle pulls may be oiled-wet, if it gets wet, it dries by itself and the problem goes away.
* The pads of the wheel on the other side the vehicle pulls may be oiled-wet, if it gets wet, it dries by itself and the problem if it is oiled it needs to clean or chance.
* Tire pressures are not equal,
*Disc brake; from the caliper piston,if it is a drum brake, there may be hydraulic oil leakage from the brake cylinder of the wheel, in this case, sufficient hydraulic pressure and brake force will not be created for that wheel,
*Crush in brake hose-pipes, etc. congestion as a result
*The pads used on two wheels are of different types (the friction coefficients are different),
*The front arrangement of the vehicle is broken (rotation adjustment, etc.),
* If shrinkage occurs due to the lubrication of the pads, it should be checked whether there is an oil leak from the axle seals, and whether there is an oil leak from the differential.
* If shrinkage occurs due to the lubrication of the pads, it should be checked whether there is an oil leak from the axle seals, and whether there is an oil leak from the differential.
Brake Grasping (Holds to Brake Pressure Suddenly)
The possible causes of the malfunction of the brake pedal, which is very sensitive and grabbing even when the brake is pressed, and stopping the vehicle suddenly, are as follows:
*Brake servo (hydrovac) may be defective, (air passage valves and springs inside the servo may be broken),
*The gap adjustment between the brake servo and the brake pedal is broken,
*Drum and brake disc are scratched, bent, turning into a asperity.
*Brake hydraulic oil may have leaked into the pads (in this case, the leak may be from the brake hose, caliper piston, wheel brake cylinder, it needs to be changed), the pads should also be replaced,
*Brake pads may be greased, sticking effect may occur, pads should be replaced,
*Using the wrong pad.
Excessive Brake Pedal Gap
When the brake pedal is pressed, the braking effect occurs after the brake pedal has traveled a great distance. The causes of excessive pedal gap are:
*There is air in the brake system,
*There is a gap-loosening in the brake pedal connection mechanism,
*The gap adjustment between the brake pedal and the brake booster is broken,
*In the disc brake system, the brake disc rotates wobbly, this wobble action pushes the caliper piston too much,
*Low quality unsuitable brake fluid, or insufficient brake fluid level,
*Fault in the self-adjustment mechanism in drum brakes (usually at the rear), or leakage in the wheel cylinder seal,
(Disc Brake System)
Brake Fluid Decrease (Brake Fluid Decrease Problem)
When the brake fluid is low, the brake system weakens, the brakes become air, the “STOP” and (or) handbrake warning lamp on the instrument panel lights up.
The reasons for the vehicle's brake oil reduction are as follows;
* In drum brake (on the rear wheels), deterioration of the wheel brake cylinder, oil leakage,
*The loosening of the wheel brake cylinder, slanting-uneven installation, uneven operation and the resulting bending of the rod pushing the piston (between the shoe and the cylinder), the slanting of the piston seal and oil leakage. Or oil leakage because it is completely worn out,
Oil leakage from brake hydraulic pipes, hoses, fittings (clamps and records),
*In the disc brake, oil leakage from the caliper piston,
* As a result of the wear of the pads, there is more hydraulic oil in the hydraulic system and the level in the oil tank decreases.
Causes of Vibration in the Brake Pedal
*If the brake discs are wobbly, the cone wears out, the disc must be ground or replaced.
* In the drum brake system, the pads are very worn (in old systems without automatic clearance adjustment), or mechanical defects in the drum brake plate,
* extreme thickness of the brake disc,
*Deformation of drum surface in drum brake,
* Deterioration of the wheel bearing. Brake Pedal Drop
If the brake pedal falls, that is, when the brake pedal is released, it stays down and does not return to its original position, the brake performance will decrease and the brakes will not hold well.
Reasons for the brake pedal to fall:
*There is a problem in the mechanical connections of the brake pedal,
* In the drum brake system, the pads are very worn (in old systems without automatic clearance adjustment), or mechanical defects in the drum brake plate,
*Breaking air (air has entered the brake hydraulic line), in this case the brakes will hold little or not at all, the brake pedal will not harden,
* Wear-faulty main brake cylinder,
*Decreased or depleted hydraulic oil in the brake system (in the brake hydraulic oil reservoir tank)
Self-Braking of a Single Wheel (Sealing)
In the drum brake system; The wheel brake cylinder pushes the brake shoes and pad and presses the drum, when the brake pedal is released, the return springs pull the shoe back and separate it from the drum. If the brake of a wheel is jammed, it means that the shoe-pad cannot be separated from the drum.
Reasons for a wheel to jam;
* Inability to move freely due to the fact that the shoe settings are too tight or rusted,
* If the return springs connected to the shoes are very weak, broken-broken or displaced,
*The brake hydraulic pipe or hose is crushed, making it difficult for the oil to pass,
*The pad is rubbing against the drum as a result of the wheel bearing wobbling,
*As a result of deterioration of the roundness of the drum, it rubs against the lining during turns.
Brake Pedal Too Soft (Brake pedal softening)
There is an air insede of the brake system or there is faulty in the brake servo. A blowing noise when the brake is pressed, the brakes do not hold, the brake pedal is too hard or soft are due to a brake servo (westinghouse) failure. As a result of air entering the brake hydraulic system (breathing of the brakes), the brake pedal becomes too soft and the brakes hold very little. It is compressing (stretching) inside the hydraulic pipes, whereas the movement must be transmitted directly without compression or stretching. If there is air in the brake system, bleed should be applied and the brake hydraulic oil should be completed, and the cause of the system's airing should be investigated and eliminated.
Vehicle Doesn't Stop Without Pressing the Brake Too Hard (Brake pedal requires a lot of force)
* In the drum brake system, unadjusted shoes cause this problem.
* In addition, a malfunction of the brake servo (hydrovac) will make the brake pedal very hard, and a great foot force will be required for braking. Brake booster vacuum hose should be checked first.
* In disc brakes, the caliper piston is jammed,
*The pads are lubricated,
*As a result of overloading the brakes, the pads may shine and glass due to excessive heat. In this case, although the pads are not finished yet, they will not create braking force, it will be necessary to press the pedals a lot. In this case, the linings should be replaced or the surfaces of which were etched and the vitrified layer should be scraped off; If it is disc, the brake disc should be checked for curvature-taper-thickness, if necessary, disc grinding or if it is too thin, disc replacement should be done, If it is a drum brake, if the drum contact surface has bending-dishing, the drum should be sent for grinding or, if necessary, replaced.

